Professional Manual Blood Pressure Cuffs⁚ A Comprehensive Guide

This comprehensive guide delves into the world of professional manual blood pressure cuffs, exploring their types, advantages, disadvantages, and proper usage; Discover how these instruments are utilized in healthcare settings, and gain insights into choosing the right cuff for your needs. We’ll also discuss accuracy, calibration, maintenance, and the role of these cuffs in both professional and home settings.
Introduction
Blood pressure is a fundamental vital sign that provides crucial information about the health of an individual’s cardiovascular system. Accurately measuring blood pressure is essential for diagnosing and managing various health conditions, including hypertension, hypotension, and cardiovascular disease. While digital blood pressure monitors have gained popularity, professional manual blood pressure cuffs, also known as aneroid sphygmomanometers, remain a staple in healthcare settings.
These instruments offer a traditional and reliable method for measuring blood pressure, relying on the principles of auscultation and manual inflation and deflation. Manual blood pressure cuffs are often preferred by healthcare professionals due to their accuracy, versatility, and ability to provide a more comprehensive assessment of a patient’s blood pressure. This guide will delve into the intricacies of professional manual blood pressure cuffs, exploring their types, advantages, disadvantages, and proper usage. We will also discuss accuracy, calibration, maintenance, and the role of these cuffs in both professional and home settings.
Types of Blood Pressure Cuffs
The world of blood pressure cuffs encompasses a variety of types, each designed for specific purposes and patient populations. While this guide focuses on professional manual blood pressure cuffs, understanding the broader landscape of cuff types is essential. Here’s a breakdown⁚
- Manual Blood Pressure Cuffs (Aneroid Sphygmomanometers)⁚ These traditional instruments rely on a manual pump, a gauge (aneroid manometer), and a stethoscope to measure blood pressure. They are widely used by healthcare professionals due to their accuracy and versatility. The cuff is inflated manually using a bulb, and the pressure is measured by listening for Korotkoff sounds through a stethoscope.
- Digital Blood Pressure Cuffs⁚ These devices automate the inflation and deflation process, providing a digital readout of blood pressure readings. They are convenient for home use but may not be as accurate as manual cuffs, especially in certain situations.
- Wrist Blood Pressure Cuffs⁚ Worn on the wrist, these cuffs offer portability but are generally less accurate than upper arm cuffs. They may be suitable for occasional monitoring but are not recommended for frequent or critical blood pressure measurements.
The choice of cuff type depends on the specific application, user preference, and individual needs. For accurate and reliable blood pressure measurements in professional settings, manual blood pressure cuffs remain the gold standard.
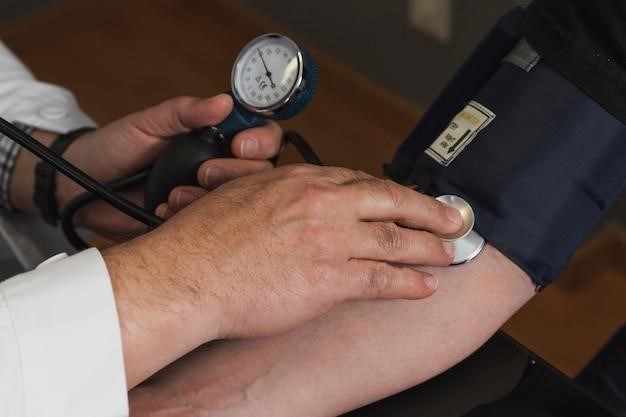
Manual Blood Pressure Cuffs⁚ The Basics
Manual blood pressure cuffs, also known as aneroid sphygmomanometers, are a mainstay in healthcare settings, offering a reliable method for measuring blood pressure. They consist of several key components⁚
- Cuff⁚ The cuff itself is a fabric or nylon bladder that wraps around the upper arm. It’s designed to fit snugly and evenly, ensuring accurate pressure application.
- Inflation Bulb⁚ This bulb allows for manual inflation of the cuff, building pressure within the bladder.
- Aneroid Manometer⁚ This gauge displays the pressure level in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). It features a dial with markings for both systolic and diastolic readings.
- Air Release Valve⁚ This valve controls the deflation rate of the cuff, allowing for gradual release of pressure.
- Stethoscope⁚ A stethoscope is essential for listening to Korotkoff sounds, the distinct sounds that indicate blood flow through the brachial artery. These sounds are used to determine systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Using a manual blood pressure cuff requires practice and proper technique to ensure accurate readings. Healthcare professionals are trained in the use of these instruments, ensuring consistent and reliable blood pressure measurements for patient care.
Advantages of Manual Blood Pressure Cuffs
Manual blood pressure cuffs offer several advantages that make them a valuable tool in healthcare settings and even for individuals seeking precise readings at home.
- Accuracy⁚ When used correctly, manual blood pressure cuffs are highly accurate, offering reliable readings for diagnosing and monitoring blood pressure conditions. They are often considered the gold standard for blood pressure measurement.
- Cost-Effective⁚ Compared to digital blood pressure monitors, manual cuffs are generally more affordable, making them a practical choice for healthcare facilities and individuals on a budget.
- Durability⁚ Manual cuffs are designed to withstand frequent use and are less prone to malfunction compared to electronic devices, making them a reliable long-term investment.
- Portability⁚ Manual cuffs are compact and lightweight, making them easy to transport for home use or in mobile healthcare settings, such as those used by paramedics or EMTs.
- No Batteries Required⁚ Manual cuffs operate without batteries or electricity, ensuring their functionality even in situations where power is limited.
- Independence⁚ Manual cuffs empower individuals to take control of their health by enabling them to monitor their blood pressure independently.
These advantages make manual blood pressure cuffs a valuable tool for healthcare professionals, allowing them to provide accurate and efficient blood pressure monitoring for their patients.
Disadvantages of Manual Blood Pressure Cuffs
While manual blood pressure cuffs offer accuracy and affordability, they also have some drawbacks that users should consider.
- Skill Required⁚ Using a manual cuff effectively requires proper training and practice. It involves listening for heart sounds with a stethoscope and accurately interpreting the readings, which can be challenging for beginners. This skill level may make them less suitable for individuals who lack experience or have difficulty hearing.
- Time-Consuming⁚ Taking a blood pressure reading with a manual cuff can be more time-consuming than using a digital monitor, particularly for individuals who are not familiar with the process.
- Potential for Error⁚ If the cuff is not positioned correctly or if the user makes mistakes in the inflation or deflation process, the readings may be inaccurate. This emphasizes the importance of proper training and practice.
- Not Ideal for Home Use⁚ While manual cuffs can be used at home, they are generally not recommended for routine self-monitoring. Digital monitors are often more convenient and user-friendly for home use.
- Stethoscope Required⁚ Manual cuffs require the use of a stethoscope to listen for heart sounds, which adds to the cost and complexity of the process.
Despite these disadvantages, manual blood pressure cuffs remain a valuable tool in healthcare settings where accuracy and reliability are paramount. Proper training and practice are essential for obtaining accurate readings with manual cuffs;
Choosing the Right Manual Blood Pressure Cuff
Selecting the appropriate manual blood pressure cuff is crucial for obtaining accurate readings. Consider the following factors when making your choice⁚
- Intended Use⁚ Determine whether the cuff will be used in a professional setting (hospital, clinic) or for home use. Professional cuffs may have features like larger dials for easier reading or durability for frequent use. Home cuffs may prioritize user-friendliness and convenience.
- Cuff Size⁚ Ensure the cuff fits the arm circumference of the individual. Cuffs are available in various sizes, ranging from adult to pediatric. An improperly sized cuff can lead to inaccurate readings.
- Calibration⁚ Look for cuffs that are calibrated to ensure accuracy. Professional cuffs are typically calibrated regularly. For home use, consider checking the cuff’s accuracy against a validated monitor at a healthcare provider’s office.
- Materials⁚ Cuffs are made from various materials, including nylon, vinyl, and latex. Choose a material that is comfortable, durable, and suitable for the intended use. Consider latex-free options for individuals with allergies.
- Inflation System⁚ Manual cuffs typically have an inflation bulb and a deflation valve. Ensure the inflation system is easy to use and provides smooth inflation and deflation. Look for a cuff with a clear gauge that is easy to read.
- Stethoscope Compatibility⁚ If you plan to use a stethoscope with the cuff, ensure they are compatible. Some cuffs may have a specific type of connector.
- Price⁚ Manual blood pressure cuffs vary in price. Consider your budget and the features you need. Professional cuffs may be more expensive than home use models.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a manual blood pressure cuff that meets your specific requirements and ensures accurate measurements.
How to Use a Manual Blood Pressure Cuff
Using a manual blood pressure cuff requires a bit of practice and familiarity with the process. Here’s a step-by-step guide⁚
- Prepare⁚ Ensure the cuff is properly calibrated and the stethoscope is clean. Have the patient sit comfortably with their arm supported at heart level.
- Position the Cuff⁚ Wrap the cuff snugly around the patient’s upper arm, about 1-2 inches above the elbow. Make sure the cuff is centered over the brachial artery. The arrow on the cuff should point towards the brachial artery.
- Inflate the Cuff⁚ Place the stethoscope over the brachial artery, just below the cuff; Gradually inflate the cuff until the pulse is no longer audible. Continue inflating for about 20-30 mmHg beyond the point where the pulse disappears.
- Deflate the Cuff⁚ Slowly deflate the cuff while listening carefully for the first sound of the pulse. This is the systolic pressure (top number). Continue deflating until the pulse disappears completely. This is the diastolic pressure (bottom number).
- Record the Readings⁚ Record the systolic and diastolic pressures in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Repeat the process if necessary, allowing a few minutes between readings.
It’s important to practice using a manual blood pressure cuff under the supervision of a healthcare professional to ensure accuracy and proficiency. Regular practice and proper technique are key to obtaining reliable readings.
Accuracy and Calibration
The accuracy of a manual blood pressure cuff is paramount, as it directly impacts the reliability of readings. Several factors influence accuracy, including proper technique, cuff size and placement, and regular calibration.
Cuff size is critical for accurate readings. A cuff that’s too small will give a falsely high reading, while a cuff that’s too large will result in a falsely low reading. It’s essential to use a cuff that fits snugly but comfortably around the patient’s arm.
Calibration is equally important. Manual blood pressure cuffs require periodic calibration to ensure their accuracy over time. Calibration involves comparing the cuff’s readings to a known standard, typically a mercury sphygmomanometer. Regular calibration helps maintain the cuff’s accuracy and ensures reliable blood pressure measurements.
While manual blood pressure cuffs are generally considered accurate when used correctly, it’s essential to note that even with proper technique and regular calibration, some degree of variability in readings is expected. Factors like anxiety, caffeine intake, and even the time of day can influence blood pressure readings.
Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and accuracy of a professional manual blood pressure cuff. Regular cleaning and storage practices can help prevent damage and maintain its functionality.
After each use, the cuff should be cleaned with a mild disinfectant solution. Pay particular attention to the inflation bulb and the stethoscope, as these components are prone to contamination. Allow the cuff to air dry completely before storing it.
When not in use, the cuff should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Avoid storing it in a way that could cause damage or distortion.
Regularly inspect the cuff for signs of wear and tear. Check the tubing for cracks or leaks, the inflation bulb for damage, and the stethoscope for loose or broken parts. If any damage is detected, it’s essential to replace the affected component to prevent inaccurate readings and potential safety hazards.
By following these simple maintenance and care practices, you can help ensure that your professional manual blood pressure cuff remains in top condition, providing accurate readings and serving you reliably for years to come.
Professional Applications
Professional manual blood pressure cuffs are indispensable tools in a variety of healthcare settings. Their reliability and versatility make them the preferred choice for medical professionals across numerous disciplines.
In hospitals and clinics, nurses, doctors, and other healthcare providers rely on manual cuffs for accurate blood pressure measurements during routine checkups, patient assessments, and emergency situations. Their manual operation allows for precise control over inflation and deflation, ensuring accurate readings even in challenging circumstances.
Paramedics and EMTs often utilize manual cuffs during emergency medical responses. Their portability and ease of use enable them to quickly assess patients’ vital signs, even in chaotic environments.
Manual cuffs are also frequently employed in research settings, providing a reliable method for measuring blood pressure in clinical trials and studies. Their accuracy and consistency are essential for obtaining reliable data for research purposes.
In addition to their use in traditional healthcare settings, manual cuffs are gaining popularity in alternative medicine practices. Acupuncturists, naturopaths, and other practitioners often utilize manual cuffs to monitor blood pressure as part of their treatment protocols.
Home Use
While professional manual blood pressure cuffs are primarily used in healthcare settings, they are also becoming increasingly popular for home use. This trend is driven by a growing awareness of the importance of monitoring blood pressure at home, particularly for individuals with hypertension or other cardiovascular conditions.
Manual cuffs offer several advantages for home use⁚
- Accuracy⁚ Manual cuffs, when used correctly, can provide highly accurate blood pressure readings, comparable to those obtained in a doctor’s office.
- Affordability⁚ Manual cuffs are generally more affordable than their electronic counterparts, making them a cost-effective option for home monitoring.
- Control⁚ Manual cuffs allow users to have complete control over the inflation and deflation process, ensuring a comfortable and personalized experience.
However, it’s crucial to remember that using a manual cuff requires some skill and practice. Individuals interested in using a manual cuff at home should receive proper training from a healthcare professional to ensure accurate readings and safe operation.
Moreover, manual cuffs may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain medical conditions or physical limitations may find electronic monitors easier to use. Ultimately, the best type of blood pressure monitor depends on individual needs and preferences.
Professional manual blood pressure cuffs remain a valuable tool in healthcare, offering a reliable and accurate method for measuring blood pressure. Their accuracy, affordability, and control over the measurement process make them a preferred choice for healthcare professionals in various settings. While they require some skill and practice to use effectively, they provide a precise and consistent way to assess a patient’s cardiovascular health.
For individuals seeking to monitor their blood pressure at home, manual cuffs can be a viable option, particularly if they are comfortable with manual devices and have received proper training. However, it’s essential to consider individual needs and preferences, as electronic monitors may be a more suitable choice for some individuals. Ultimately, the choice between manual and electronic blood pressure monitors depends on a combination of factors, including personal preference, budget, and specific healthcare needs.
Regardless of the type of blood pressure monitor chosen, it’s crucial to ensure its accuracy and reliability. Regular calibration and proper use are essential for obtaining accurate readings and making informed decisions about cardiovascular health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if my home blood pressure cuff is accurate?
While most home blood pressure monitors are generally reliable, it’s a good idea to have your monitor checked for accuracy by a healthcare professional. They can compare your readings to those taken with their professional equipment to ensure your monitor is providing accurate results.
Are manual blood pressure cuffs accurate?
When used correctly, manual blood pressure cuffs can be very accurate. However, they require proper technique and training to ensure precise readings. It’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and seek guidance from a healthcare professional if you’re unsure about the proper usage.
Do cheap blood pressure cuffs work?
While inexpensive blood pressure cuffs may be available, it’s essential to prioritize quality and accuracy. Look for cuffs from reputable brands that are clinically validated. Investing in a reliable cuff can ensure accurate readings and contribute to your overall health management.